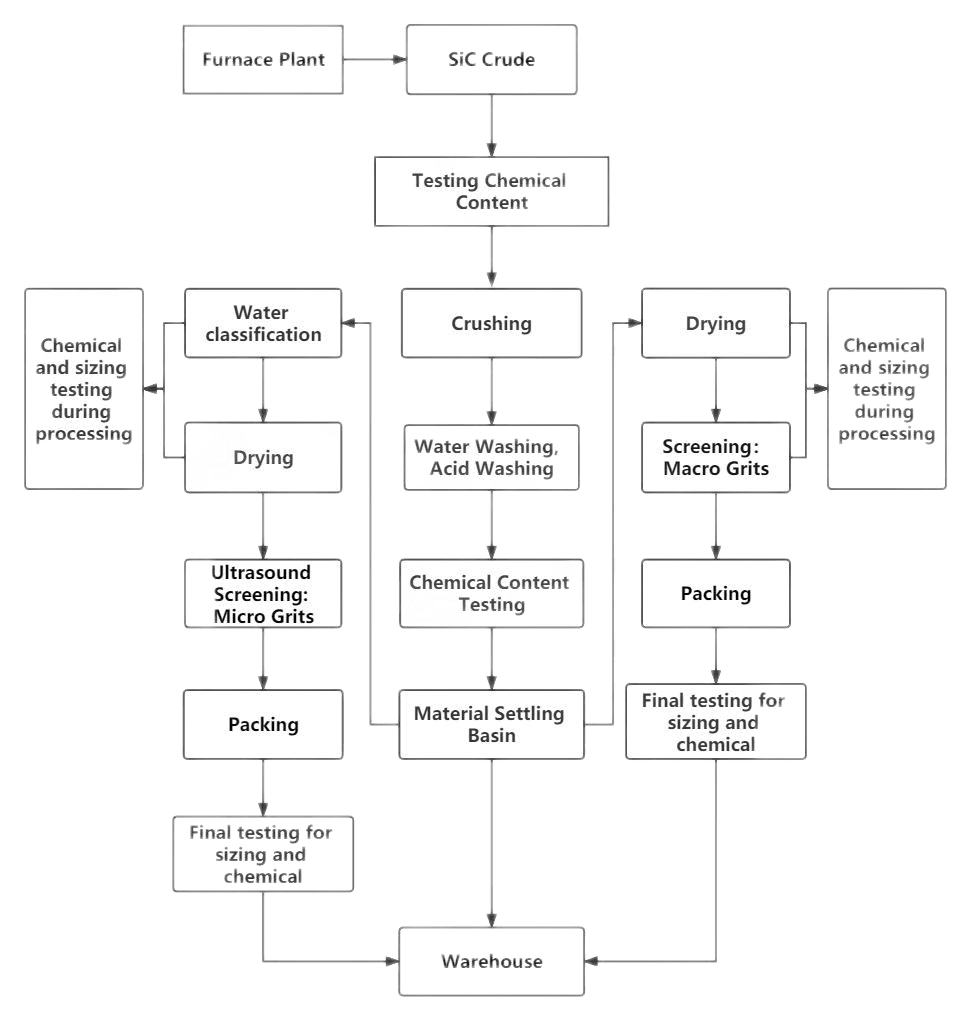
Manufacturing Process of Silicon Carbide
The manufacturing process of silicon carbide involves several steps, ensuring the production of high-quality and reliable materials.
Raw Materials
The primary raw materials used in silicon carbide manufacturing are silicon and carbon. These materials are carefully selected and undergo a rigorous purification process to eliminate impurities and achieve the desired composition.
Powder Preparation
After the raw materials have been purified, they are converted into fine powders through various techniques. Silicon and carbon powders are mixed in precise proportions to achieve the desired composition of silicon carbide. The powders are then milled and ground to obtain a uniform particle size distribution, ensuring consistency in the final product.
Mixing and Shaping
In this stage, the silicon carbide powders are mixed with binders and additives to enhance their workability and formability. The mixture is then shaped into the desired form using different techniques such as pressing, extrusion, or slip casting. This step allows manufacturers to create a wide range of products, from intricate ceramic components to abrasive grains for grinding applications.
Sintering
Sintering is a critical process that involves heating the shaped silicon carbide at high temperatures, typically in a controlled atmosphere or under vacuum conditions. During sintering, the powders bond together, resulting in a dense and solid material with improved mechanical properties. The sintering temperature and duration are carefully controlled to achieve the desired density and structural integrity of the final product.
Finishing and Quality Control
After sintering, the silicon carbide products undergo additional processing and finishing steps to meet specific requirements. This may include grinding, polishing, or coating to achieve the desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Quality control measures, such as inspections, testing, and analysis, are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that the silicon carbide products meet the required standards and specifications.

Applications of Silicon Carbide
Silicon carbide finds applications in a wide range of industries due to its exceptional properties and versatility. Some of the key application areas include:
Abrasives and Grinding
Silicon carbide’s exceptional hardness and abrasion resistance make it an ideal choice for abrasive materials. It is used in the production of grinding wheels, cutting tools, and abrasive papers, providing superior performance and extended tool life in various machining and surface finishing operations.
Ceramics and Refractories
Silicon carbide’s high strength, excellent thermal shock resistance, and resistance to chemical attack make it a valuable material in the production of ceramics and refractory products. It is used in kiln furniture, crucibles, and high-temperature components, enabling reliable performance in extreme heat and corrosive environments.
Electronics and Semiconductors
Silicon carbide has gained significant attention in the field of electronics and semiconductors. Its unique electrical properties, such as high breakdown voltage, high thermal conductivity, and wide bandgap, make it suitable for power electronic devices, LED lighting, and high-temperature electronics.
Automotive and Transportation
The automotive industry is increasingly adopting silicon carbide for various applications. It is used in the manufacturing of components such as brake discs, clutches, and engine parts, offering superior performance, weight reduction, and improved fuel efficiency. Silicon carbide-based power electronics are also revolutionizing electric vehicle charging systems, enabling faster charging and increased power density.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Silicon Carbide
Advantages
- Exceptional hardness and abrasion resistance
- High thermal conductivity and heat dissipation
- Low thermal expansion and dimensional stability
- Excellent chemical resistance
- Wide bandgap and high-temperature operation capabilities
- Enhanced electrical properties for power electronics
Disadvantages
- Relatively high production cost compared to other materials
- Limited availability of large-sized components
- Processing challenges due to the hardness and brittleness of silicon carbide